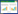扩展功能
文章信息
- 李瑛琦, 龚劲松, 许正宏, 史劲松
- LI Ying-Qi, GONG Jin-Song, XU Zheng-Hong, SHI Jin-Song
- Ⅲ型类人胶原蛋白在大肠杆菌重组表达及发酵制备
- Recombinant expression and fermentation of type Ⅲ human-like collagen in Escherichia coli
- 微生物学通报, 2020, 47(12): 4154-4171
- Microbiology China, 2020, 47(12): 4154-4171
- DOI: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.200070
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2020-01-29
- 接受日期: 2020-03-24
- 网络首发日期: 2020-07-28
2. 江南大学生物工程学院 粮食发酵工艺与技术国家工程实验室 江苏 无锡 214122
2. National Engineering Laboratory for Cereal Fermentation Technology, School of Biotechnology, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu 214122, China
胶原蛋白是哺乳动物体内含量最多的功能性蛋白[1]。胶原蛋白由3条α链的多肽链亚基组成,α链自身构型为左手螺旋,三条α链又互相缠绕成右手螺旋结构,即胶原蛋白的“胶原域”[2]。胶原蛋白的一级结构分析结果显示,其肽链由(Gly-X-Y)n组成,其中X通常是脯氨酸,Y通常是羟脯氨酸[3]。按照胶原蛋白发现的先后顺序,可将其分为Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型、Ⅲ型等28种胶原蛋白[4],Ⅰ型胶原蛋白分子组成为[α1(Ⅰ)]2α2(Ⅰ),主要分布于骨骼中[5];Ⅱ型胶原蛋白由[α1(Ⅱ)]3组成,主要由软骨细胞产生,因其含有大量赖氨酸残基,因而糖基化率较高[6];Ⅲ型胶原蛋白分子组成为[α1(Ⅲ)]3,因含半胱氨酸所以肽链间形成二硫键,因此其本身就可形成细纤维,Ⅲ型胶原蛋白血管中含量较高,主要存在于肺泡间质中且分布杂乱,因而形成复杂的网状结构,正是这种结构使得肺组织具有良好的柔韧性与弹性,并且可以为细胞提供充足养分,使得皮肤饱满透亮[7]。
目前胶原蛋白的生产方法主要包括3种:(1)传统提取法。即动物组织如猪皮、牛皮等的酸碱处理法,此法具有操作简单、生产时间短、回收率高等优点,但得到的胶原蛋白成分复杂,可能含有一定的免疫原成分,限制了其在医学组织材料领域的普遍应用[8-9];(2)化学合成法。2006年,Kotch等通过化学法合成了具有胶原蛋白特征序列(Gly-X-Y)n的多肽,并且可以成功自组装为三螺旋结构[10],然而此方法在批量制备和成本控制方面,近十多年来并未取得突破;(3)基因工程法。这是目前技术发展最快的胶原蛋白生产方法,可以通过基因工程技术,选用昆虫[11]、转基因烟草[12]、大肠杆菌[13]、毕赤酵母[14]等各种宿主细胞生产胶原蛋白,不仅可以避免病毒隐患、免疫排斥反应等缺点,获得更高的亲水性及安全性[15],而且可以在新型的分子设计软件指导下,对胶原蛋白的空间构型和性能进行个性化设计。
本研究设计了编码分子量为13.6 kD的人源Ⅲ型胶原蛋白基因kit,构建大肠杆菌表达菌株并进行了表达,通过发酵罐上扩大培养提升Ⅲ型类人胶原蛋白的产量,并借助超滤初纯及亲和层析等策略提高蛋白纯度,最终采用N端测序、氨基酸分析、质谱分析及圆二色谱等分析方法表征所表达获得的类人胶原蛋白。本研究制备的类人胶原蛋白表达避免了传统提取法所带来的动物疾病或病毒等潜在隐患以及免疫排斥反应,具有优良的医学性能,同时其发酵法制备工艺可以使生产成本及产品质量得到有效控制,也易于实现规模化生产。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料 1.1.1 菌株和质粒菌种E.coli BL21(DE3)、人源胶原蛋白基因kit及表达质粒pET-28a(+)由本实验室保藏。人源胶原蛋白基因kit是根据人Ⅲ型胶原蛋白α1链mRNA序列,选定胶原肽段Gly-X-Y,将Pro之外的部分疏水氨基酸进行亲水性氨基酸的相似性替换设计而成。
1.1.2 主要试剂和仪器PCR引物由亦欣生物科技(无锡)有限公司合成;DNA ladder、DNA marker购于杭州宝赛生物科技有限公司;Premix TaqTM DNA聚合酶购于Takara公司;限制性内切酶、羊抗鼠IgG HRP、化学发光底物SuperSignal、抗生素KanR和IPTG购于Thermo Fisher Scientific公司。电泳仪购于Bio-Rad公司;低温冷冻离心机购于Eppendorf公司;pH计购于Sartorius公司;镍琼脂糖凝胶色谱柱HisTrap HP (1 mL)纯化柱购于GE公司;酵母粉、蛋白胨购于Oxoid公司。
1.1.3 培养基LB培养基(g/L):Tryptone 10.0,Yeast Extract 5.0,NaCl 10.0。
发酵培养基(g/L):Tryptone 12.0,Yeast Extract 24.0,K2HPO4 16.4,KH2PO4 2.3,Glycerin 20.0,pH 6.8。
补料培养基(g/L):Tryptone 60.0,Yeast Extract 120.0,K2HPO4 82.2,KH2PO4 11.6,Glycerin 333.0,pH 6.8。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 引物设计与合成根据类人胶原蛋白(human-like collagen,HLC)的基因序列,设计并合成引物。kit-F:5′-CGGGATCCAGAGGTCCACCCGGTGAGC-3′;kit-R:5′-CGGAATTCTTAACCACCGGCTGGA CCTTGG-3′。
1.2.2 表达质粒pET-28a(+)-kit的构建采用pUC57-kit质粒为模板,以kit-F及kit-R为引物,PCR扩增基因kit。PCR反应条件:95 ℃ 5 min;95 ℃ 30 s;55 ℃ 30 s;72 ℃ 30 s,35个循环;72 ℃ 5 min;12 ℃ 12 h。PCR反应体系:Premix TaqTM DNA聚合酶25 μL,模板1 μL,kit-F (10 μmol/L) 1 μL,kit-R (10 μmol/L) 1 μL,ddH2O 22 μL。将PCR产物及pET-28a(+)质粒用BamH I和EcoR I双酶切,过夜连接后转化至E.coli BL21(DE3)中,挑取阳性转化子,通过菌液PCR验证、双酶切(BamH I/EcoR I)验证及测序验证后进行斜面保藏。
1.2.3 重组菌pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21(DE3)的表达对斜面保藏的菌株进行活化后37 ℃、220 r/min培养,当OD600为1.0时,使用终浓度为0.2 mmol/L的IPTG 20 ℃诱导20 h,对发酵液进行SDS-PAGE分析及Western blotting检测胶原蛋白含量。
Western blotting鉴定方法:将重组蛋白进行SDS-PAGE,在电流的作用下,使蛋白质从PAGE胶转印至固相载体聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)膜上,封闭1 h使抗体只能和特异的蛋白质结合,过夜孵育一抗(小鼠抗聚组氨酸单克隆抗体,1:1 000稀释),使用TBST洗涤后孵育二抗1 h (羊抗鼠IgG-HRP,1:1 000稀释),TBST充分洗涤,加入化学发光底物SuperSignal检测试剂,选用Image Lab软件通过凝胶成像仪进行曝光拍照。
蛋白含量测定方法:Bradford法测定菌体总蛋白后,使用Quantity One软件扫描SDS-PAGE电泳图,分析出重组蛋白占总蛋白的比例,再根据菌体总蛋白量与重组蛋白的百分含量计算出重组蛋白含量[16]。
1.2.4 类人胶原蛋白的发酵及纯化利用7 L发酵系统进行类人胶原蛋白的发酵,以Invitrogen公司的大肠杆菌发酵手册为参考,设置以下发酵条件:pH 6.8,溶解氧(dissolved oxygen,DO) > 20%,37 ℃,400 r/min。待OD600为8.0时用终浓度为0.2 mmol/L的IPTG 20 ℃诱导36 h结束发酵。将菌体低温超声破碎(破碎4 s,停止6 s,共破碎15 min)处理后,破碎液上清经超滤离心管初步纯化后通过0.22 μm纤维滤膜过滤,使用HisTrap HP 1 mL镍柱通过线性洗脱的方式进行亲和层析AKTA (Binding buffer:0.5 mol/L NaCl,20 mmol/L Tris-HCl,20 mmol/L咪唑,pH 7.9;Elution buffer:0.5 mol/L NaCl,20 mmol/L Tris-HCl,0.5 mol/L咪唑,pH 7.9),收集洗脱液,采用3 kD的超滤管对洗脱液进行脱盐处理,冻干得到类人胶原蛋白纯品。
1.2.5 类人胶原蛋白的N端测序采用蛋白多肽测序仪分析类人胶原蛋白N端的15个氨基酸,由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司完成。
1.2.6 类人胶原蛋白的氨基酸分析对类人胶原蛋白水溶液使用6 mol/L HCl进行酸水解,通过邻苯二甲醛(o-phthalic dicarboxaldehyde)和氯甲酸芴甲酯(FMOC-Cl)联用的衍生化后,使用高效液相色谱经C18柱分离后分析氨基酸含量。
1.2.7 类人胶原蛋白的质谱分析采用基质辅助激光解吸电离飞行时间质谱(matrix assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrometry,MALDI-TOF-MS)对类人胶原蛋白水溶液进行相对分子量测定。
1.2.8 类人胶原蛋白的圆二色谱分析蛋白质肽键的紫外光吸收范围是185−240 nm。采用圆二色谱仪表征类人胶原蛋白,条件如下:带宽:1 nm;响应值:1 s;测量范围:250−190 nm;扫描速度:100 nm/min;溶剂:去离子水。
2 结果与分析 2.1 基因工程菌的构建对构建成功的基因工程菌进行菌液PCR验证,并提取质粒进行双酶切验证(图 1),从图 1中可以看出,菌液PCR与质粒双酶切均获得大小约为320 bp的基因片段,DNA测序结果表明质粒构建成功。
|
| 图 1 类人胶原蛋白表达载体验证结果 Figure 1 Validation results of human-like collagen expression vector 注:M:DL5000 DNA Marker;1:pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21菌液PCR验证;2:pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21质粒双酶切验证(BamH I/EcoR I). Note: M: DL5000 DNA Marker; 1: pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21 bacterial solution PCR verification; 2: pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21 plasmid double digestion verification (BamH I/EcoR I). |
|
|
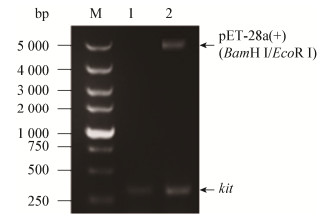
对构建成功的表达质粒进行摇瓶发酵,超声破碎菌体,对细胞破碎液进行SDS-PAGE及Western blotting验证,通过蛋白含量计算得出类人胶原蛋白表达量约为0.53 g/L,结果见图 2和图 3。从图 2、3中可以看出,目的蛋白表观分子量大小约为27 kD左右,但其实际分子量大小为13.6 kD,推测原因可能是类人胶原蛋白中亲水氨基酸较多,导致蛋白与SDS结合能力变弱,负电荷减少使电泳迁移距离变短,因而表观分子量变大[17]。
|
| 图 2 类人胶原蛋白摇瓶发酵SDS-PAGE验证结果 Figure 2 SDS-PAGE validation results of human-like collagen fermentation by shake flask 注:M:蛋白分子标准;1:pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21全细胞破碎液;2:pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21细胞破碎液上清;3:pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21细胞破碎液沉淀;4:pET-28a(+)/BL21全细胞破碎液(对照). Note: M: Protein Marker; 1: pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21 whole cell disruption solution; 2: pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21 cell disruption supernatant; 3: pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21 cell disruption solution precipitation; 4: pET-28a(+)/BL21 whole cell disruption solution (control). |
|
|

|
| 图 3 类人胶原蛋白摇瓶发酵Western blotting验证结果 Figure 3 Western blotting validation results of human-like collagen fermentation by shake flask 注:M:蛋白分子标准;1:pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21细胞破碎液上清;2:pET-28a(+)/BL21细胞破碎液上清(对照). Note: M: Protein Marker; 1: pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21 cell disruption supernatant; 2: pET-28a(+)/BL21 cell disruption supernatant (control). |
|
|
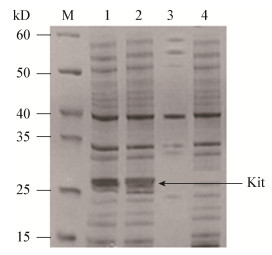
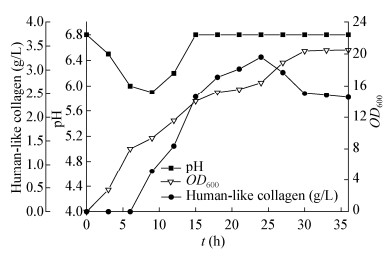
在7 L发酵罐中对类人胶原蛋白采用pH-stat法补料发酵,通过控制补料使其pH保持在6.8,在细菌对数生长中后期使用终浓度为0.2 mmol/L的IPTG诱导36 h,其中类人胶原蛋白表达量达到3.02 g/L (图 4)。发酵结束后,高压匀浆破碎菌体,4 ℃、10 000 r/min离心10 min得到破碎液上清,对上清采用超滤浓缩管初步纯化后,使用0.22 μm纤维滤膜过滤上清后进行蛋白纯化,经SDS-PAGE及Quantity One软件分析得出最终类人胶原蛋白纯度约为91% (图 5)。
|
| 图 4 类人胶原蛋白7 L罐上补料发酵 Figure 4 Fed-batch fermentation mode for production of human-like collagen on a 7 L fermentor |
|
|

|
| 图 5 类人胶原蛋白AKTA纯化液的SDS-PAGE分析 Figure 5 SDS-PAGE analysis of human-like collagen purified solution by AKTA 注:M:蛋白分子标准;1:pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21蛋白纯化液. Note: M: Protein Marker; 1: pET-28a(+)-kit/BL21 protein purification solution. |
|
|
蛋白质N端的序列直接影响其整体的生物学功能。类人胶原蛋白N端分析结果为:NH2-Gly-Pro-Pro-Gly-Glu-Pro-Gly-Asn-Pro-Gly-Ser-Pro-Gly-Asn-Gln,与预期蛋白N端序列结果一致。
2.5 类人胶原蛋白的氨基酸分析氨基酸分析可以用于测定蛋白质、肽及氨基酸的含量。氨基酸分析结果如表 1所示,从表 1中可以看出,类人胶原蛋白中甘氨酸、脯氨酸及谷氨酸含量较多,胶原蛋白区别于其他蛋白最主要的特点是甘氨酸与脯氨酸含量较多,而谷氨酸含量多的原因则是酸水解技术导致谷氨酰胺转化为谷氨酸。
| 氨基酸 Amino acid |
含量 Content (mg/mL) |
百分比 Percentage (%) |
| Asp | 0.27 | 8.36 |
| Glu | 0.52 | 16.04 |
| Ser | 0.08 | 2.51 |
| His | 0.06 | 1.84 |
| Gly | 1.28 | 39.27 |
| Thr | 0.15 | 4.57 |
| Ala | 0.05 | 1.54 |
| Met | 0.05 | 1.46 |
| Lys | 0.09 | 2.85 |
| Pro | 0.70 | 21.56 |
| Arg | − | − |
| Tyr | − | − |
| Cys | − | − |
| Val | − | − |
| Phe | − | − |
| Ile | − | − |
| Leu | − | − |
| 总计Total | 3.26 | 100.00 |
| 注:−:未检出. Note: −: not checked out. | ||
MALDI-TOF-MS可以准确分析出类人胶原蛋白的分子量,从图 6可以看出,类人胶原蛋白实际分子量为13 135.0 Da,与理论分子量一致。
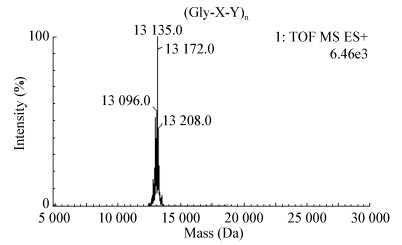
|
| 图 6 类人胶原蛋白MALDI-TOF-MS分析 Figure 6 MALDI-TOF-MS analysis of human-like collagen |
|
|
天然胶原蛋白的圆二色谱特征一般是在197 nm处有一个负吸收峰,在225 nm处有一个微弱的正吸收峰,吸收峰位置会随着氨基酸的长度和序列的变化而偏移[18]。由图 7可知,制备的类人胶原蛋白符合天然胶原蛋白谱图特征。
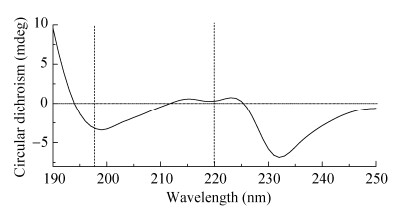
|
| 图 7 类人胶原蛋白圆二色谱分析 Figure 7 CD analysis of human-like collagen |
|
|
重组胶原蛋白具备极好的生物兼容性及生物活性,已广泛应用于生物及医药领域。Guo等利用类人胶原蛋白HLC与转谷氨酰胺酶(transglutaminase,TG)交联得到可承载碱性成纤维细胞生长因子(basic fibroblast growth factor,bFGF)的水凝胶,实验证明HLC/TG水凝胶对bFGF和细胞具有良好的生物相容性[19];马淑骅等证明重组人源胶原蛋白可以修复激光受损的小鼠皮肤[20];江山聚源生物科技有限公司已将重组胶原蛋白应用于美容化妆品、营养保健品及医疗器械等方面[21]。
鉴于胶原蛋白所具备的优良特性和应用价值,同时为避免动物来源产品的高风险,重组人胶原蛋白的发酵制备受到了广泛关注,至今已有20多年的研究历史。早在1999年,Toman等将37 kb的胶原蛋白基因片段和αS1-乳腺酪蛋白特异性启动子基因片段共同转化入小鼠分泌型乳腺,生产出8 mg/mL人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白[22];日本广岛大学的Adachi等把人Ⅰ型胶原蛋白基因转入至蚕细胞中,通过蚕的绢丝腺同时分泌人胶原蛋白与绢丝蛋白,但其人胶原蛋白表达量只有1%左右,长度只占人胶原蛋白长度的1/5[23];Tang等在大肠杆菌中成功表达一段类人胶原蛋白基因,最终产量为0.26 g/L[24]。
为了进一步提高重组人胶原蛋白的表达量及纯度,近年来不同的发酵、基因工程及制备策略已被采用。范代娣等将人Ⅱ型胶原蛋白基因片段拼接后转化至大肠杆菌中,通过高密度发酵得到29.4%的胶原蛋白[25];南京理工大学的高立虎通过基因串联技术构建了六串联体Ⅲ型类人胶原蛋白提高表达量[1];王晓军等将类人胶原蛋白发酵液依次经DEAE-52和Sephadex G-100柱层析分离纯化后,最终的产物纯度可以达到98%[26]。
本论文通过基因工程技术,设计类人胶原蛋白基因kit并在E.coli中获得了成功表达,通过发酵罐上的扩大培养,Ⅲ型类人胶原蛋白的产量可以达到3.02 g/L,通过超滤初纯及亲和层析,最终得到了纯度约为91%的类人胶原蛋白。通过N端测序、氨基酸分析、质谱分析及圆二色谱分析表征类人胶原蛋白,实验证明类人胶原蛋白成功表达。然而本研究所制备的类人胶原蛋白的产量及纯度仍有提升空间,未来可通过发酵优化、基因串联及多步纯化的方法有望获得产量和纯度更高、分子量及用途不同的类人胶原蛋白,将进一步提升其工业应用价值。
| [1] |
Gao LH. Construction of human repeat-like collagen expression vector and its secretory expression in Pichia pastoris[D]. Nanjing: Master's Thesis of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2007 (in Chinese) 高立虎.重复序列类人胶原蛋白表达载体的构建及在毕赤酵母中的分泌表达[D].南京: 南京理工大学硕士学位论文, 2007 |
| [2] |
Jiang TD. Collagen and Collagen Peptide[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2006. (in Chinese) 蒋挺大. 胶原与胶原蛋白[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2006. |
| [3] |
Jenkins CL, Raines RT. Insights on the conformational stability of collagen[J]. Natural Product Reports, 2002, 19(1): 49-59. DOI:10.1039/a903001h |
| [4] |
Rasmussen M, Jacobsson M, Björck L. Genome-based identification and analysis of collagen-related structural motifs in bacterial and viral proteins[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003, 278(34): 32313-32316. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M304709200 |
| [5] |
Winston RL, Fitzgerald MC. Mass spectrometry as a readout of protein structure and function[J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews, 1997, 16(4): 165-179. DOI:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2787(1997)16:4<165::AID-MAS1>3.0.CO;2-F |
| [6] |
Xiao JX, Madhan B, Li YJ, et al. Osteogenesis imperfecta model peptides: incorporation of residues replacing Gly within a triple helix achieved by renucleation and local flexibility[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2011, 101(2): 449-458. DOI:10.1016/j.bpj.2011.06.017 |
| [7] |
Persikov AV, Pillitteri RJ, Amin P, et al. Stability related bias in residues replacing glycines within the collagen triple helix (Gly-Xaa-Yaa) in inherited connective tissue disorders[J]. Human Mutation, 2004, 24(4): 330-337. DOI:10.1002/humu.20091 |
| [8] |
Sadowska M, Kołodziejska I, Niecikowska C. Isolation of collagen from the skins of Baltic cod (Gadus morhua)[J]. Food Chemistry, 2003, 81(2): 257-262. DOI:10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00420-X |
| [9] |
Giménez B, Turnay J, Lizarbe MA, et al. Use of lactic acid for extraction of fish skin gelatin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2005, 19(6): 941-950. DOI:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2004.09.011 |
| [10] |
Kotch FW, Raines RT. Self-assembly of synthetic collagen triple helices[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(9): 3028-3033. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0508783103 |
| [11] |
Nokelainen M, Helaakoski T, Myllyharju J, et al. Expression and characterization of recombinant human type Ⅱ collagens with low and high contents of hydroxylysine and its glycosylated forms[J]. Matrix Biology, 1998, 16(6): 329-338. DOI:10.1016/S0945-053X(98)90004-X |
| [12] |
Ruggiero F, Exposito JY, Bournat P, et al. Triple helix assembly and processing of human collagen produced in transgenic tobacco plants[J]. FEBS Letters, 2000, 469(1): 132-136. DOI:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01259-X |
| [13] |
Buechter DD, Paolella DN, Leslie BS, et al. Co-translational incorporation of trans-4-hydroxyproline into recombinant proteins in bacteria[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2003, 278(1): 645-650. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M209364200 |
| [14] |
Werten MWT, Wisselink WH, Jansen-van den Bosch TJ, et al. Secreted production of a custom-designed, highly hydrophilic gelatin in Pichia pastoris[J]. Protein Engineering, Design and Selection, 2001, 14(6): 447-454. DOI:10.1093/protein/14.6.447 |
| [15] |
Wang Y, Cui FZ, Zhai Y, et al. Investigations of the initial stage of recombinant human-like collagen mineralization[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2006, 26(4): 635-638. DOI:10.1016/j.msec.2005.07.019 |
| [16] |
Chen G, Wu M, Wang G, et al. Expression of recombinant human collagen peptide in E.coli[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2011, 37(4): 656-660. (in Chinese) 陈光, 吴铭, 王刚, 等. 重组人胶原蛋白肽在大肠杆菌中的高效表达[J]. 吉林大学学报:医学版, 2011, 37(4): 656-660. |
| [17] |
Cho Y, Gorina S, Jeffrey PD, et al. Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: understanding tumorigenic mutations[J]. Science, 1994, 265(5170): 346-355. DOI:10.1126/science.8023157 |
| [18] |
Zhang ZB, Wang JJ, Chen HJ, et al. Study of collagen mimetic peptide's triple-helix structure and its thermostability by circular dichroism[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2014, 34(4): 1050-1055. (in Chinese) 张之宝, 王静洁, 陈晖娟, 等. 圆二色谱研究胶原模拟多肽三螺旋结构及其热稳定性[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2014, 34(4): 1050-1055. DOI:10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)04-1050-06 |
| [19] |
Guo YY, Xu B, Wang YH, et al. Dramatic promotion of wound healing using a recombinant human-like collagen and bFGF cross-linked hydrogel by transglutaminase[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition, 2019, 30(17): 1591-1603. DOI:10.1080/09205063.2019.1652416 |
| [20] |
Ma SY, Sun YN, Yang WF, et al. Repair effect and mechanism of recombinant human collagen on laser induced damage of mice skin[J]. Acta Laser Biology Sinica, 2018, 27(5): 399-406. (in Chinese) 马淑骅, 孙娅楠, 杨伟峰, 等. 重组人源胶原蛋白对激光损伤小鼠皮肤修复作用及机制研究[J]. 激光生物学报, 2018, 27(5): 399-406. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2018.05.003 |
| [21] |
Yang SL, Liu B, Gao LH, et al. A recombinant human-derived collagen and its preparation method: CN, 201110327865.5[P]. 2012-05-09 (in Chinese) 杨树林, 刘斌, 高立虎, 等.一种重组人源胶原蛋白及其制备方法: 中国, 201110327865.5[P]. 2012-05-09 |
| [22] |
Toman PD, Pieper F, Sakai N, et al. Production of recombinant human type Ⅰ procollagen homotrimer in the mammary gland of transgenic mice[J]. Transgenic Research, 1999, 8(6): 415-427. DOI:10.1023/A:1008959924856 |
| [23] |
Adachi T, Tomita M, Shimizu K, et al. Generation of hybrid transgenic silkworms that express Bombyx mori prolyl- hydroxylase α-subunits and human collagens in posterior silk glands: Production of cocoons that contained collagens with hydroxylated proline residues[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2006, 126(2): 205-219. DOI:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.04.035 |
| [24] |
Tang YP, Yang XL, Hang BJ, et al. Efficient production of hydroxylated human-like collagen via the co-expression of three key genes in Escherichia coli Origami (DE3)[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2016, 178(7): 1458-1470. DOI:10.1007/s12010-015-1959-6 |
| [25] |
Fan DD, Duan MR, Mi Y, et al. High density fermentation of recombinant E.coli for production of human-like collagen[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2002, 53(7): 752-754. (in Chinese) 范代娣, 段明瑞, 米钰, 等. 重组E.coli工程菌高密度培养生产人源型胶原蛋[J]. 化工学报, 2002, 53(7): 752-754. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0438-1157.2002.07.019 |
| [26] |
Wang XJ, Hui JF, Mi Y, et al. Separation and purification of recombinant human collagen-like protein[J]. Chinese Journal of Biologicals, 2003, 16(4): 212-214. (in Chinese) 王晓军, 惠俊峰, 米钰, 等. 重组类人胶原蛋白的分离纯化[J]. 中国生物制品学杂志, 2003, 16(4): 212-214. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-5503.2003.04.006 |
 2020, Vol. 47
2020, Vol. 47