扩展功能
文章信息
- 贾红岩, 王亚涛, 张芝华, 冯娜, 刘艳芳, 周帅, 张忠, 张劲松, 唐庆九
- JIA Hong-Yan, WANG Ya-Tao, ZHANG Zhi-Hua, FENG Na, LIU Yan-Fang, ZHOU Shuai, ZHANG Zhong, ZHANG Jing-Song, TANG Qing-Jiu
- 高效液相色谱法测定不同产地及品种灵芝三萜类成分的含量
- Determination of triterpenoids in Ganodema lingzhi from different areas and species by HPLC
- 微生物学通报, 2017, 44(1): 238-244
- Microbiology China, 2017, 44(1): 238-244
- DOI: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.160112
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2016-01-29
- 接受日期: 2016-04-14
- 优先数字出版日期(www.cnki.net): 2016-05-04
2. 上海海洋大学食品学院 上海 201306;
3. 上海应用技术学院 上海 201418
2. College of Food Science, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China;
3. Shanghai Institute of Technology, Shanghai 201418, China
灵芝(Ganodema lingzhi)在我国历史悠久,是一种药用价值很高的中药材。近年来的分子生物学证据表明,我国的栽培灵芝是模式产地属于中国的灵芝新种Ganodema lingzhi Sheng H. Wu, Y. Cao & Y.C. Dai[1-2],属于真菌界担子菌门伞菌纲多孔菌目灵芝科灵芝属的成员[3],俗称“仙草”、“还魂草”,一直被视为滋补强身、延年益寿的珍贵药材。现代医学表明,灵芝具有调节免疫力、抗肿瘤、抗衰老、保肝、提高机体耐缺氧能力等活性[4-5],对于治疗高血压、高血脂、肝病、心血管疾病等具有良好的临床疗效[6]。
灵芝具有多种活性物质。三萜类化合物是其主要的活性物质之一。灵芝中三萜类化合物种类很多,目前统计,国内外研究人员已分离出一百多种三萜成分[7-8]。灵芝酸A和灵芝酸B是1982年首次从灵芝中分离出的三萜类化合物[9]。药理研究表明,灵芝三萜具有解毒、保肝、抗肿瘤、抗炎、抗氧化、抗组织胺释放、抑制血管紧张素、调节免疫力等功效[10-11]。比色法[12-13]和高效液相色谱法[14-20]是灵芝三萜定量分析的主要方法,其中比色法用齐墩果酸或熊果酸为对照品,测得总三萜的含量往往与实际含量有较大差别,HPLC法具有分离效果好、重现性好、灵敏度高等优点,目前广泛用于灵芝三萜的测定方法中。但由于灵芝酸的标准品难以分离纯化,国内HPLC法测定灵芝三萜成分的文献中,所建方法测定一种三萜酸或几种三萜酸的较多,王筱婧等[20]建立了测定灵芝酸C2的HPLC方法,董虹玲[14]等、姚松君[21]建立了同时测定灵芝酸C2、灵芝酸G和灵芝酸A三种三萜酸的方法,李保明[16]等建立了同时测定9种三萜酸的方法等。灵芝三萜类化合物的测定方法有两个标准:NY/SJ 339-2001和NY/T 2278-2012。NY/SJ 339-2001标准具有误差大、试剂干扰等不足;NY/T 2278-2012标准仅适用于灵芝酸A和灵芝酸B的HPLC方法测定。本文在实验室分离纯化多种三萜标准品的基础上,建立了同时测定灵芝三萜中包括酸性部分和中性部分的12种三萜标准品高效液相色谱梯度洗脱的方法,通过方法学检验,该方法简单、精密度高、重复性好,并用此方法测定了不同产地及品种灵芝子实体三萜类成分的含量。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料福建省产地:菌草鹿角状灵芝(FJ)国家菌草工程技术研究中心提供;浙江省产地:生产119 (ZJ);安徽省产地:黄山1号(AH);吉林省产地:赤芝(JL-1),野生灵芝1 (JL-2),野生灵芝2 (JL-3)。
1.2 主要试剂灵芝酸C2、灵芝酸B、灵芝酸A、灵芝酮三醇、灵芝酸DM、灵芝酸T、灵芝醇B、灵芝酸S、灵芝酸G、灵芝酸F、灵芝酸D、灵芝稀酸B等三萜标准品购自美国Sigma公司;色谱纯乙腈,美国Dikma公司;甲醇、冰醋酸,国药集团药业股份有限公司;水为超纯水。
1.3 主要仪器Waters 600型高效液相色谱仪系统:在线脱气,四元泵,Waters 717 plus自动进样器,柱温箱,Waters 2996型二极管阵列检测器,Empower色谱工作站及数据处理系统,美国Waters公司;KQ-600B型超声清洗器,昆山市超声仪器有限公司;ELGA PURELAB Ultra超纯水仪,威立雅水处理技术(上海)有限公司;5415D微型离心机,德国Eppendorf公司;MS105DU电子分析天平,瑞士Metter Toledo公司;小型粉碎机,上海淀九中药机械制造有限公司。
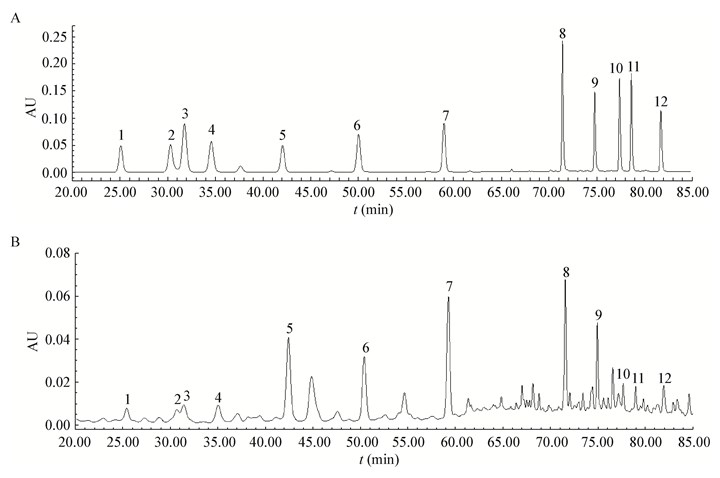
1.4 实验方法 1.4.1 高效液相色谱条件: 选用Agilent ZORBAX SB-Aq (4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm)色谱柱,以乙腈-醋酸(0.01%)水溶液为流动相进行梯度洗脱,流速1.0 mL/min,190 nm−400 nm 3D数据采集,柱温30,进样量20 μL,分析波长为252 nm,梯度洗脱程序:乙腈(A)-醋酸(0.01%)水溶液(B):0→25 min,A:28%→30%;25→50 min,A:30%→39%;50→60 min,A:39%→60%;60→85 min,A:60%→100%;85→100 min,A:100%;100→ 101 min,A:100%→28%;101→110 min,A:28%。 1.4.2 标准品溶液的制备: (1)单标溶液的配制:精密称取干燥至恒重的12种三萜标准品:灵芝酸C2、灵芝酸B、灵芝酸A、灵芝酮三醇GT-2、灵芝酸DM、灵芝酸T、灵芝醇B、灵芝酸S、灵芝酸G、灵芝酸F、灵芝酸D、灵芝稀酸B各适量,分别加入甲醇配制成1 g/L的标准品储备液,备用。 (2)系列混合标准品溶液的制备:精密量取上述单一标准品溶液各适量,置于25 mL容量瓶中,加入甲醇稀释至刻度,制成含灵芝酸C2 (100 mg/L)、灵芝酸B (100 mg/L)、灵芝酸A (100 mg/L)、灵芝酮三醇GT-2 (105 mg/L)、灵芝酸DM (100 mg/L)、灵芝酸T (95 mg/L)、灵芝酸B (100 mg/L)、灵芝酸S (105 mg/L)、灵芝酸G (112 mg/L)、灵芝酸F (130 mg/L)、灵芝酸D (106 mg/L)、灵芝稀酸B (100 mg/L)的混合标准品溶液,并稀释成6个系列浓度混合标准品溶液,备用。 1.4.3 样品溶液的制备: 分别取粉碎后的样品0.5 g,置于10 mL带塞的试管中,精确加入10 mL无水乙醇,密塞,摇匀,连续超声(功率600 W,频率40 kHz)提取1 h,冷却至室温,补足失重,摇匀,移取2.0 mL于离心管中,13 200 r/min离心2 min,移取上清液,过0.22 μm微孔有机相滤膜,滤液供HPLC分析用。 2 结果与分析 2.1 三萜类标准样品的定性分析将三萜类成分的单一标准品溶液与1.4.2(2)项中的混合标准品溶液分别进样分析,根据三萜类成分的保留时间定性,三萜混合标准品图谱及样品(菌草鹿角状灵芝)的分析图谱,结果如图 1所示。由图 1可知,在上述色谱条件下,各色谱峰分离度良好,12种三萜类标准样品的保留时间分别为灵芝酸C2:24.43±0.01 min;灵芝酸G:24.42±0.01 min;灵芝稀酸B:30.90±0.00 min;灵芝酸B:33.71±0.01 min;灵芝酸A:41.22±0.01 min;灵芝酸D:49.12±0.01 min;灵芝酸F:58.16±0.02 min;灵芝酮三醇:70.88±0.01 min;灵芝酸DM:74.17±0.01 min;灵芝酸S:78.75±0.01 min;灵芝酸T:78.01±0.01 min;灵芝醇B:81.04±0.01 min。
|
| 图 1 三萜类标准品混合组分与样品的HPLC图谱 Figure 1 Chromatogram of mixture of triterpenoids standards and tested sample 注:A:标准品;B:样品. 1:灵芝酸C2;2:灵芝酸G;3:灵芝稀酸B;4:灵芝酸B;5:灵芝酸A;6:灵芝酸D;7:灵芝酸F;8:灵芝酮三醇;9:灵芝酸DM;10:灵芝酸S;11:灵芝酸T;12:灵芝醇B. Note: A: Standard; B: Sample. 1: Ganoderic acid C2; 2: Ganoderic acid G; 3: Ganoderenic acid B; 4: Ganoderic acid B; 5: Ganoderic acid A; 6: Ganoderic acid D; 7: Ganoderic acid F; 8: Ganodermanontriol; 9: Ganoderic acid DM; 10: Ganoderic acid S; 11: Ganoderic acid T; 12: Ganoderiol B. |
|
|
| 标准溶液 Standard samples |
回归方程 Regressive equations |
相关系数 Correlative coefficient |
线性范围 Linear bounds (mg/L) |
| 灵芝酸C2 Ganoderic acid C2 | Y=1.36e+004 X-7.82e+003 | 1.000 0 | 3.125-100 |
| 灵芝酸G Ganoderic acid G | Y=1.58e+004 X-1.26e+004 | 0.999 8 | 3.500-112 |
| 灵芝稀酸B Ganoderenic acid B | Y=3.02e+004 X-1.17e+004 | 0.999 9 | 3.125-100 |
| 灵芝酸B Ganoderic acid B | Y=1.91e+004 X-1.37e+004 | 0.999 9 | 3.125-100 |
| 灵芝酸A Ganoderic acid A | Y=1.43e+004 X-9.73e+003 | 1.000 0 | 3.125-100 |
| 灵芝酸D Ganoderic acid D | Y=1.81e+004 X-5.21e+003 | 0.999 9 | 3.312-106 |
| 灵芝酸F Ganoderic acid F | Y=1.54e+004 X-4.21e+003 | 1.000 0 | 4.062-130 |
| 灵芝酮三醇Ganodermanontriol | Y=2.61e+004 X-2.04e+004 | 1.000 0 | 3.281-105 |
| 灵芝酸DM Ganoderic acid DM | Y=1.63e+004 X-2.54e+003 | 0.999 9 | 3.125-100 |
| 灵芝酸S Ganoderic acid S | Y=1.88e+004 X-4.23e+003 | 1.000 0 | 3.281-105 |
| 灵芝酸T Ganoderic acid T | Y=2.17e+004 X-2.25e+003 | 1.000 0 | 2.968-95 |
| 灵芝醇B Ganoderiol B | Y=1.49e+004 X-1.33e+003 | 1.000 0 | 3.125-100 |
| 三萜化合物 Triterpenoids |
精密度 Precision (%) |
重复性 Repeatability (%) |
稳定性 Stability (%) |
平均回收率 Recovery (%) |
RSD (%) |
| 灵芝酸C2 Ganoderic acid C2 | 1.38 | 0.37 | 2.34 | 102.98 | 0.75 |
| 灵芝酸G Ganoderic acid G | 0.37 | 1.36 | 1.13 | 100.38 | 1.63 |
| 灵芝稀酸B Ganoderenic acid B | 0.50 | 0.42 | 1.03 | 102.49 | 1.28 |
| 灵芝酸B Ganoderic acid B | 1.80 | 0.36 | 1.47 | 102.10 | 1.18 |
| 灵芝酸A Ganoderic acid A | 0.58 | 0.77 | 1.34 | 97.31 | 1.38 |
| 灵芝酸D Ganoderic acid D | 0.53 | 0.37 | 0.73 | 101.28 | 2.40 |
| 灵芝酸F Ganoderic acid F | 1.70 | 0.38 | 0.82 | 99.53 | 1.84 |
| 灵芝酮三醇Ganodermanontriol | 0.15 | 0.36 | 2.41 | 101.11 | 2.76 |
| 灵芝酸DM Ganoderic acid DM | 0.31 | 0.56 | 2.08 | 100.20 | 0.94 |
| 灵芝酸S Ganoderic acid S | 1.03 | 0.34 | 0.69 | 101.83 | 1.32 |
| 灵芝酸T Ganoderic acid T | 1.06 | 0.43 | 1.77 | 100.57 | 0.60 |
| 灵芝醇B Ganoderiol B | 1.58 | 1.26 | 1.15 | 100.53 | 1.53 |
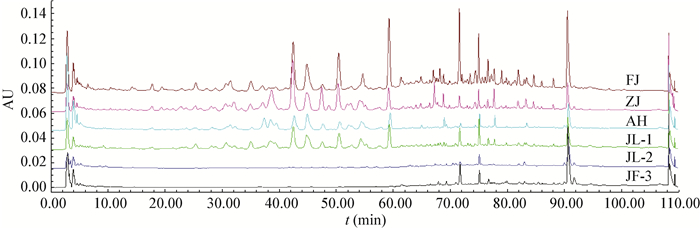
精确称取待测样品各两份,按1.4.3项方法制备样品溶液,按上述色谱条件进行测定,通过样品HPLC色谱图洗脱峰的保留时间与标准样对比,得出待测样品所含三萜的种类,外标曲线法计算各样品中所含三萜的含量,结果见表 3和图 2。
| 样品名称Sample | FJ | ZJ | AH | JL-1 | JL-2 | JL-3 |
| 灵芝酸C2 Ganoderic acid C2 | 266.70±0.57 | 205.26±0.95 | 111.44±0.80 | 174.92±2.92 | - | - |
| 灵芝酸G Ganoderic acid G | 283.26±1.28 | 330.11±0.33 | 45.67±0.90 | 159.68±2.97 | - | - |
| 灵芝稀酸B Ganoderenic acid B | 180.78±0.37 | 201.82±0.97 | 53.49±0.32 | 35.53±0.44 | - | - |
| 灵芝酸B Ganoderic acid B | 326.45±0.84 | 231.51±1.40 | 60.94±0.37 | 231.98±0.66 | - | - |
| 灵芝酸A Ganoderic acid A | 1 716.97±0.35 | 1 904.63±0.69 | 591.74±0.83 | 803.04±0.79 | 29.21±0.96 | - |
| 灵芝酸D Ganoderic acid D | 926.91±1.28 | 749.27±0.66 | 224.54±2.44 | 420.36±0.57 | - | - |
| 灵芝酸F Ganoderic acid F | 1 591.44±0.45 | 529.33±0.72 | 366.10±3.03 | 542.14±0.65 | 14.79±0.46 | 36.14±0.59 |
| 灵芝酮三醇Ganodermanontriol | 630.54±0.07 | 141.92±0.95 | 25.08±0.22 | 178.61±0.78 | 51.88±1.04 | 186.91±0.08 |
| 灵芝酸DM Ganoderic acid DM | 614.94±1.39 | 191.95±1.16 | 132.77±2.86 | 215.45±3.25 | 126.47±0.56 | 122.46±1.09 |
| 灵芝酸S Ganoderic acid S | 168.79±0.75 | 219.17±0.92 | 15.61±1.45 | 17.29±0.13 | 23.36±0.63 | 18.18±0.71 |
| 灵芝酸T Ganoderic acid T | 15.98±1.27 | 41.25±0.68 | 113.22±1.11 | 5.47±1.02 | 11.56±1.00 | 5.14±0.39 |
| 灵芝醇B Ganoderiol B | 316.13±0.26 | 129.43±0.87 | 11.32±1.22 | 58.11±0.92 | 39.28±0.50 | 33.27±0.18 |
| 总量Total amount | 7 248.83±0.72 | 4 875.64±2.36 | 1 751.92±1.14 | 2 842.58±0.98 | 296.55±1.15 | 402.10±0.09 |
| 注:数据均为两次测定的平均值±标准差;−:代表未检出. Note: All results are means of three determinations; −: Not detected. |
||||||
|
| 图 2 不同产地灵芝子实体的HPLC图谱 Figure 2 Chromatogram of theG. lingzhi from different areas |
|
|
通过对不同产地中12种三萜成分含量测定发现,不同产地中所含三萜类成分在组成和含量上有显著差异。以福建的菌草鹿角状灵芝中的灵芝酸含量最高,野生灵芝中灵芝酸含量较低;栽培灵芝12种灵芝酸中灵芝酸A所占比例最高,FJ、ZJ、AH、JL-1灵芝品种中灵芝酸A分别占灵芝酸总量的23.69%、39.06%、33.78%、28.25%;同时比较了从吉林省收集的野生灵芝中三萜的含量,结果发现,所收集的野生灵芝中仅含有少量的灵芝酸F、灵芝酮三醇、灵芝酸DM、灵芝酸S、灵芝酸T、灵芝酸B,JL-2中检测出少量的灵芝酸A。
3 讨论目前,国内外文献对灵芝酸D、灵芝酸F、灵芝酮三醇的HPLC测定报道较少。本文在张圣龙[22]实验方法的基础上开发了包含这3种三萜成分在内同时测定灵芝酸C2、灵芝酸B、灵芝酸A、灵芝酮三醇GT-2、灵芝酸DM、灵芝酸T、灵芝醇B、灵芝酸S、灵芝酸G、灵芝酸F、灵芝酸D、灵芝稀酸B等12种三萜成分的高效液相色谱法。此方法涉及到中草药与食药用菌中12种常见的三萜类成分,与目前关于灵芝子实体中三萜类成分测定的高效液相色谱法相比,本研究测定的三萜类成分种类多、分离度高、覆盖面广,具有较强的代表性、参考性和实用价值。方法学考察结果显示,该方法灵敏度高、重复性与稳定性好,适用于灵芝子实体中12种三萜类成分的测定分析,为评价灵芝子实体的质量提供了测定方法和手段。
三萜类成分是评价灵芝质量的指标之一,通过分析比较发现不同来源的灵芝三萜含量差别较大,高达3倍以上,这可能与多种因素有关。开发保健食品等新产品要选择活性较高的原料,本文可为新产品的开发提供借鉴。同时我们发现吉林长白山上采集的野生灵芝与吉林的栽培灵芝相比,三萜含量远远低于栽培灵芝,总三萜的含量仅为栽培灵芝的十分之一。所测原料中,如果从三萜含量来评定灵芝的质量,野生灵芝的价值要低于栽培灵芝,是否野生灵芝在其他成分方面有差异,还需进行进一步的研究。
| [1] | Dai YC, Cao Y, Zhou LW, et al. Notes on the nomenclature of the most widely cultivated Ganoderma species in China[J]. Mycosystema 2013, 32(6) : 947–952. (in Chinese) 戴玉成, 曹云, 周丽伟, 等. 中国灵芝学名之管见[J]. 菌物学报 2013, 32(6) : 947–952. |
| [2] | Cao Y, Wu SH, Dai YC. Species clarification of the prize medicinal Ganoderma mushroom "Lingzhi"[J]. Fungal Diversity 2012, 56(1) : 49–62. DOI:10.1007/s13225-012-0178-5 |
| [3] | Shao LP, Shen RX, Zhang SX, et al. Fungus Taxonomy[M]. Beijing: Forestry, 1983 . (in Chinese) 邵力平, 沈瑞祥, 张素轩, 等. 真菌分类学[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1983 . |
| [4] | Zhang XY, Yang CQ. The chemical composition and pharmacological action of Ganoderma lucidum[J]. Foreign Medical Sciences (Herbal Drug) 2006, 21(4) : 152–155. (in Chinese) 张晓云, 杨春清. 灵芝的化学成分和药理作用[J]. 国外医药(植物药分册) 2006, 21(4) : 152–155. |
| [5] | Feng DJ. The chemical composition, efficacy and pharmacological action of Ganoderma lucidum[J]. Special Economic Animal and Plant 2006, 9(8) : 39–40. (in Chinese) 冯道俊. 灵芝的化学成分、功效及药理作用[J]. 特种经济动植物 2006, 9(8) : 39–40. |
| [6] | Gan WW, Chang JD. Study on extraction of polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidumusing response surface methodology[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences 2009(1) : 259–262. (in Chinese) 干伟伟, 常继东. 灵芝多糖提取条件的响应曲面法优化研究[J]. 江苏农业科学 2009(1) : 259–262. |
| [7] | Lin ZB. Modern Research of Ganoderma Lucidum[M].3rd Edition. Beijing: Medical Publishing House of Peking University, 2007: 199 -244. (in Chinese) 林志彬. 灵芝的现代研究[M].3版. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2007: 199 -244. |
| [8] | Chen RY, Yu DQ. Advances in studies on chemical constituents on Ganoderma triterpene[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 1990, 25(12) : 940–953. (in Chinese) 陈若芸, 于德泉. 灵芝三萜化学成分研究进展[J]. 药学学报 1990, 25(12) : 940–953. |
| [9] | Kubota T, Asaka Y, Miura I, et al. Structures of ganoderic acid A and B, two new lanostane type bitter triterpenes from Ganoderma lucidum (Fr.) Karst[J]. Helvetica Chimica Acta 1982, 65(2) : 611–619. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1522-2675 |
| [10] | Huang YJ, Xiao GL. The progress of pharmacology on ganoderma triterpene[J]. Cuiding Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy 2008, 14(9) : 87–88, 97. (in Chinese) 黄艳娟, 肖桂林. 灵芝三萜药理学作用研究进展[J]. 中医药导报 2008, 14(9) : 87–88, 97. |
| [11] | Xu JW, Zhao W, Zhong JJ. Biotechnological production and application of ganoderic acids[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2010, 87(2) : 457–466. DOI:10.1007/s00253-010-2576-5 |
| [12] | Fu LZ, Wu XQ, Li MY, et al. Crude polysaccharide and triterpene content of ganoderma fruit bodies at different stages of development[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi 2008, 15(3) : 47–50. (in Chinese) 付立忠, 吴学谦, 李明焱, 等. 灵芝不同生长发育期粗多糖和三萜含量变化规律[J]. 食用菌学报 2008, 15(3) : 47–50. |
| [13] | Fu LZ, Wu XQ, Li MY, et al. Analysis and evaluation of polysaccharides and triterpenes contents of fruitbody of Ganoderma lucidum strains[J]. Edible Fungi of China 2009, 28(4) : 38–40. (in Chinese) 付立忠, 吴学谦, 李明焱, 等. 灵芝品种子实体多糖和三萜含量分析与评价[J]. 中国食用菌 2009, 28(4) : 38–40. |
| [14] | Dong HL, Xia GP, Zhao NX, et al. Quantitative analysis of ganoderic acid C2, G, and A in sporophore and spore powder of Ganoderma by HPLC[J]. Drugs & Clinic 2013, 28(1) : 41–43. (in Chinese) 董虹玲, 夏广萍, 赵娜夏, 等. HPLC法测定灵芝子实体和孢子粉中灵芝酸C2、灵芝酸G和灵芝酸A[J]. 现代药物与临床 2013, 28(1) : 41–43. |
| [15] | Xing ZT, Yu QH, Zhang JS, et al. Comparative study on triterpenes in different Ganoderma species[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials 2004, 27(8) : 575–576. (in Chinese) 邢增涛, 郁琼花, 张劲松, 等. 不同品种灵芝中三萜类化合物的比较研究[J]. 中药材 2004, 27(8) : 575–576. |
| [16] | Li BM, Gu HF, Li Y, et al. Determination of nine triterpenoid acids from Ganoderma lucidum of different producting areas by HPLC[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica 2012, 37(23) : 3599–3603. (in Chinese) 李保明, 古海锋, 李晔, 等. HPLC测定不同产地灵芝中9种三萜酸[J]. 中国中药杂志 2012, 37(23) : 3599–3603. |
| [17] | Ma L, Wu F, Chen RY. Analysis of triterpene constituents from Ganoderma lucidum[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica 2003, 38(1) : 50–52. (in Chinese) 马林, 吴丰, 陈若芸. 灵芝三萜成分分析[J]. 药学学报 2003, 38(1) : 50–52. |
| [18] | Wang XM, Yang M, Guan SH, et al. Quantitative determination of six major triterpenoids in Ganoderma lucidum and related species by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2006, 41(3) : 838–844. DOI:10.1016/j.jpba.2006.01.053 |
| [19] | Li BM, Liu C, Wang HQ, et al. Study on determination method of total triterpen acid content of Ganoderma lucidum[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica 2007, 32(12) : 1234–1236. (in Chinese) 李保明, 刘超, 王洪庆, 等. 灵芝总三萜酸含量测定方法的研究[J]. 中国中药杂志 2007, 32(12) : 1234–1236. |
| [20] | Wang XJ, Lin HB, Xu J, et al. Determination of concentrations of triterpene constituents and polysaccharides in Ganoderma by HPLC and UV-VIS[J]. Contemporary Medicine 2009, 15(31) : 128–130. (in Chinese) 王筱婧, 林焕冰, 徐江, 等. HPLC法和UV-VIS法测定灵芝孢子粉中灵芝三萜及灵芝多糖的含量[J]. 当代医学 2009, 15(31) : 128–130. |
| [21] | Yao SJ. Study on technology of ultrasonic extraction of triterpenoids from Ganoderma lucidum and its fingerprint method[D]. Guangzhou: Master's Thesis of South China University of Technology, 2010: 44-64 (in Chinese) 姚松君.灵芝三萜的超声波提取工艺及其指纹图谱检测方法的研究[D].广州:华南理工大学硕士学位论文, 2010: 44-64 |
| [22] | Zhang SL. Studies on active ingredients and fingerprint of Ganoderma[D]. Hefei: Master's Thesis of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, 2013: 31-43 (in Chinese) 张圣龙.灵芝活性成分及其指纹图谱研究[D].合肥:安徽中医药大学硕士学位论文, 2013: 31-43 |
 2017, Vol. 44
2017, Vol. 44