扩展功能
文章信息
- 杨慧林, 张志斌, 颜日明, 汪涯, 朱笃
- YANG Hui-Lin, ZHANG Zhi-Bin, YAN Ri-Ming, WANG Ya, ZHU Du
- 东乡野生稻内生放线菌Streptomyces sp. PRh5 的全基因组测序及序列分析
- Whole-genome sequencing and analysis of an endophytic actinomycete Streptomyces sp. PRh5 from Dongxiang wild rice
- 微生物学通报, 2015, 42(4): 801-809
- Microbiology China, 2015, 42(4): 801-809
- 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.140615
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2014-08-14
- 接受日期: 2014-09-29
- 优先数字出版日期(www.cnki.net): 2014-10-14
2. 江西科技师范 大学 江西省生物加工过程重点实验室 江西 南昌 330013
2. Jiangxi Science&Technology Normal University,Jiangxi Key Laboratory of Bioprocess,Nanchang,Jiangxi 330013,China)
植物内生菌(Endophyte)是指那些在其生活史的一定阶段或全部阶段生活于健康植物的各种组织和器官内部的微生物,即被它们感染的宿主植物不会或至少暂时不会表现出明显的症状,并可通过组织学方法和严格表面消毒的植物组织中分离或从植物组织内直接扩增出其DNA[1,2,3]。因此,可以把植物内生菌类比于人类肠道中的正常菌群,内生菌与宿主植物协同进化、互惠共生,形成复杂的微生态体系。植物内生菌主要包括植物内生真菌、内生细菌和内生放线菌。
东乡野生稻(Oryza rufipogon Griff.)是迄今所发现的世界上分布最北的野生稻,我国三大普通野生稻之一,被列为国家二级保护植物[4]。因其具有抗寒、耐旱、耐瘠、抗虫等优良品质,研究者对其进行了广泛的研究[5,6]。作物的优良性状除了决定于优良遗传基因外,与其内生菌也具有一定的关系[7,8]。内生菌在植物内特殊生境的长期作用下,可能产生一些具有抗菌、抗肿瘤、抗病毒、增强免疫力等功效的新型化合物[9,10,11,12]。Nakashima等[13]从内生放线菌Polymorphospora rubra K07-0510中分离得到溶血抑制性化合物Trehangelins A-C,其中Trehangelins A的IC50值为0.1 g/L。Igarashi等从泰国植物Abrus pulchellus中分离得到一批内生放线菌,其中Micromonospora sp. GMKU326产生抗革兰氏阳性菌抗生素Maklamicin[14],菌株Microbispora sp. GMKU 363合成含有呋喃酮的聚酮类化合Linfuranone A[15]。
本实验室前期从东乡野生稻中分离获得的一株对细菌和真菌都具有较强抗菌活性的内生放线菌Streptomyces sp. PRh5[16],并保藏于中国典型培养物保藏中心(CCTCC No. 2013487)[17]。为了进一步深入研究Streptomyces sp. PRh5的抗菌机制,本研究采用高通量测序技术对PRh5菌株进行全基因组测序,并对该菌株的次级代谢产物合成基因簇进行预测,相关研究结果将为PRh5菌株的功能基因组学研究提供基础数据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料 1.1.1 主要试剂和仪器:酵母提取物、麦芽提取物,购自英国OXOID公司;葡萄糖、Tris、EDTA、乙醇、CaCO3、琼脂粉等,国产分析纯试剂。TGL-20M离心机,上海卢湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;ChemiDoc XRS凝胶成像系统,Bio-Rad公司;HiSeq 2000高通量测序仪,Illumina公司。 1.1.2 菌株和培养基:内生放线菌Streptomycessp. PRh5为本实验室从东乡野生稻中分离得到,保藏于中国典型培养物保藏中心(CCTCC No. 2013487);ISP2培养基(g/L):葡萄糖4.0,酵母提取物4.0,麦芽提取物10.0;固体培养基在ISP2培养基中添加CaCO3 2.0 g和琼脂粉12.0 g,加水至1 L,pH 7.2。 1.2 放线菌的培养与基因组DNA的提取Streptomyces sp. PRh5接种至斜面培养基活化(30 °C,3-4 d),然后转接至摇瓶液体培养3-5 d,抽滤收集菌体用于提取基因组DNA。采用液氮研磨方法裂解细胞壁,然后采用大连宝生物公司的基因组DNA提取试剂DNAiso (Code No. 9770A,详细步骤见产品说明书)。
1.3 基因组测序、组装及基因组注释基因组DNA提取后进行质量鉴定,在浓度和纯度达到测序要求后进行全基因组测序。构建插入片段约500 bp的PCR-free测序文库,然后采用Hiseq2000测序仪进行测序,获得约1 Gb的原始测序数据。原始数据经过预处理去除接头、引物及低质量数据后,采用Velvet 1.2.10组装软件[18]进行序列组装,通过优化参数Kmer值获得最好的组装结果。基因预测采用Glimmer 3.0软件[19],基因功能注释采用BLAST软件与NCBI的蛋白质数据库(NR)及COG数据库进行比对。
1.4 次级代谢产物合成基因簇分析次级代谢产物的编码基因通常在基因组中成簇存在,本研究采用antiSMASH软件[20,21]对Streptomyces sp. PRh5菌株中的次级代谢产物合成基因簇分析,并预测可能合成的化合物。
2 结果与分析 2.1 Streptomyces sp. PRh5菌株鉴定菌株PRh5基内菌丝由浅黄色到黄褐色,有分枝,不断裂,气生菌丝白色到灰色,孢子成螺旋状孢子链,一般为2-3圈,孢子表面粗糙。基于16S rRNA基因序列构建系统进化树显示与菌株Streptomyces indonesiensis DSM 41759T在同一个系统分支上。将菌株PRh5与Streptomyces indonesiensis DSM 41759T基因组进行DNA-DNA杂交实验,结果为54.6%,低于70%新种界限(表1),综合该菌在生理生化特征、16S rRNA基因同源性和化学指标等方面的实验结果,确定菌株PRh5是链霉菌属中的一个新种,命名为Streptomyces sp. PRh5。
| 重复 Repeats |
DSM 41759T | PRh5 | Relatedness 1 | Relatedness 2 | ||||
| Iblank | IAA | IAB | Iblank | IAA | IAB | |||
| 1 | 5 676.354 | 8 316.356 | 7 057.815 | 7 137.073 | 7 708.418 | 7 459.625 | 0.523 280 285 | 0.564 548 565 |
| 2 | 6 457.284 | 7 416.082 | 7 013.763 | 7 210.325 | 7 989.736 | 7 616.861 | 0.580 392 325 | 0.521 59 387 |
| 3 | 6 088.816 | 7 912.312 | 7 172.375 | 6 699.612 | 7 089.112 | 6 892.792 | 0.594 220 662 | 0.495 969 191 |
| 4 | 5 929.013 | 7 313.172 | 6 718.861 | 6 917.522 | 8 030.712 | 7 496.615 | 0.570 633 865 | 0.520 210 386 |
| Average | - | - | - | - | - | 0.567 131 784 | 0.525 580 503 | |
Note: Iblank: Hybridization values with salmon sperm DNA; IAA: Self-hybridization values; IAB: Hybridization values.
| Features | Streptomyces sp. PRh5 | S. violaceusniger | S. coelicolor | S. hygroscopicus | S. rapamycinicus |
| Length (bp) | 11 084 188 | 10 657 107 | 8 667 507 | 10 145 833 | 12 700 734 |
| Contigs (No.) | 290 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| GC content (%) | 71.1 | 71.0 | 72.1 | 71.9 | 69.3 |
| CDS (No.) | 8 712 | 8 482 | 7 825 | 8 849 | 10 002 |
| Average CDS size (bp) | 1 062 | 1 077 | 991 | 952 | 1 034 |
| Coding (%) | 83.5 | 85.7 | 88.9 | 83.2 | 81.5 |
| tRNA (No.) | 65 | 63 | 63 | 68 | 65 |
| GenBank No. | JABQ00000000 | NC_015957 | NC_003888 | NC_017765 | NC_022785 |

|
|
图 1 Streptomyces sp. PRh5 与Streptomyces violaceusniger Tu 4113 的共线性分析
Figure 1 Synteny analysis of Streptomyces sp. PRh5 and Streptomyces violaceusniger Tu 4113
注:sp1–sp65:Streptomyces sp. PRh5 的contig001–contig65;sv1:Streptomyces violaceusniger Tu 4113 基因组DNA. Note: sp1–sp65: Streptomyces sp. PRh5 contig001–contig65; sv1: Streptomyces violaceusniger Tu 4113 genome DNA. |
|
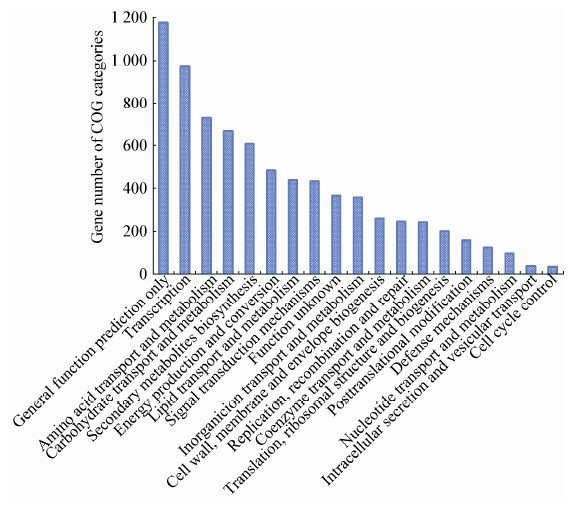
| 图 2 Streptomyces sp. PRh5 蛋白质COG 聚类分析 Figure 2 COG cluster analysis of Streptomyces sp. PRh5 proteins |
次级代谢产物的编码基因通常在基因组中成簇存在,编码具有多种功能的复合酶。其中,研究得最清楚的是PKS/NRPS基因簇。本研究采用antiSMASH软件对PRh5菌株中所有的次级代谢产物合成基因簇进行分析,共预测得到50个基因簇,其中PKS/NRPS类型基因簇有35个,约占总基因簇数量的70% (表3)。同时,对基因簇的次级代谢产物进行了预测(图3),其中包括治疗神经变性病症的美力霉素、治疗骨质疏松的雷弗霉素、新型糖肽类抗生素Mannopeptimycin、环脂肽抗生素Friulimicin及尼日利亚菌素、利迪链菌素、疏螺旋体素等20余种,表明Streptomyces sp. PRh5具有合成多种生物活性物质的能力。
| 序号 ID | 重叠群 Contig No. | 位置 Position (nt) | 基因数量 Gene amount | 基因簇类型 Gene cluster type | 预测化合物 Putative compound |
| 1 | contig001 | 1-30 660 | 19 | t1pks | Concanamycin A/刀豆素A |
| 2 | contig002 | 150 595-17 2671 | 21 | terpene | Unknown |
| 3 | contig002 | 166 384-211 804 | 33 | t1pks | Unknown |
| 4 | contig003 | 47 506-69 839 | 20 | lant | Unknown |
| 5 | contig004 | 1-28 889 | 18 | t1pks-nrps | Meridamycin/美立霉素 |
| 6 | contig005 | 113 535-135 660 | 18 | siderophore | Siderophore/铁载体 |
| 7 | contig008 | 82 347-146 391 | 38 | t1pks | Reveromycin/雷弗霉素 |
| 8 | contig009 | 48 934-56 250 | 7 | ectoine | Cobalamin/VB12 |
| 9 | contig010 | 54 522-78 542 | 23 | siderophore | Vibrioferrin/弧菌铁素 |
| 10 | contig011 | 89 721-139 750 | 37 | t1pks | Borrelidin/疏螺旋体素 |
| 11 | contig014 | 96 236-104 564 | 8 | butyrolactone | Unknown |
| 12 | contig016 | 3-35 562 | 19 | t1pks | Ansamitocin |
| 13 | contig016 | 64 757-95 971 | 32 | t3pks | Unknown |
| 14 | contig016 | 110 527-156 832 | 31 | nrps | Mannopeptimycin |
| 15 | contig018 | 125 204-149 847 | 21 | butyrolactone | Lankamycin/lankacidin |
| 16 | contig025 | 381-32 196 | 24 | t1pks | Crocacin |
| 17 | contig025 | 15 928-56 983 | 32 | lant-bcin | Streptolydigin/利迪链菌素 |
| 18 | contig025 | 44 224-122 295 | 36 | nrps | Laspartomycin/天冬霉素 |
| 19 | contig030 | 9 318-101 595 | 55 | nrps-t1pks | Friulimicin |
| 20 | contig032 | 31 874-99 781 | 18 | t1pks | Monensin/莫能菌素 |
| 21 | contig035 | 61 110-97 302 | 31 | t1pks | Rubradirin/红迪菌素 |
| 22 | contig036 | 27 375-70 631 | 39 | other | Heboxidiene |
| 23 | contig038 | 44 929-94 905 | 26 | nrps | Melanin/黑色素 |
| 24 | contig040 | 1-23 274 | 18 | t1pks | Nigericin(partial)/尼日利亚菌素 |
| 25 | contig040 | 29 261-91 923 | 32 | t1pks-nrps | Dihydrochalcomycin |
| 26 | contig041 | 35 638-60 207 | 21 | terpene | Unknown |
| 27 | contig042 | 56 114-90 186 | 23 | t1pks | Chlorothricin/氯丝菌素 |
| 28 | contig044 | 1 725-42 506 | 30 | nrps-t3pks | Unknown |
| 29 | contig048 | 58-79 694 | 45 | t1pks-nrps | Skyllamycin |
| 30 | contig049 | 1-33 122 | 15 | t1pks | Concanamycin A/刀豆素A |
| 31 | contig050 | 47 999-79 236 | 22 | siderophore | Unknown |
| 32 | contig053 | 29 198-50 737 | 15 | terpene | Unknown |
| 33 | contig069 | 555-25 526 | 19 | blactam | Clavulanic acid/Cephamycin C |
| 34 | contig072 | 70-39 794 | 30 | t1pks | Unknown |
| 35 | contig072 | 29 307-56 570 | 18 | nrps | Unknown |
| 36 | contig073 | 23 434-54 677 | 19 | nrps | Melanin |
| 37 | contig079 | 34-25 059 | 21 | nrps | Unknown |
| 38 | contig082 | 23 836-48 823 | 22 | t1pks | Meridamycin/美立霉素 |
| 39 | contig084 | 15 469-46 480 | 28 | terpene | Brasilicardin A |
| 40 | contig085 | 20 106-46 105 | 26 | t2pks | Fredericamycin/菲特霉素 |
| 41 | contig086 | 2-40 149 | 21 | t1pks | Lankamycin/lankacidin |
| 42 | contig087 | 1-44 039 | 33 | nrps-t3pks | Balhimycin |
| 43 | contig090 | 326-40 131 | 34 | nrps | Unknown |
| 44 | contig092 | 19 050-39 642 | 19 | t1pks | Kanamycin/卡那霉素 |
| 45 | contig093 | 3-39 632 | 10 | t1pks | FR-008 |
| 46 | contig094 | 16 059-38 232 | 21 | t1pks | Concanamycin A/刀豆素A |
| 47 | contig113 | 136-27 725 | 18 | terpene-t1pks | Unknown |
| 48 | contig121 | 1-25 237 | 12 | t1pks | Nigericin(partial)/尼日利亚菌素 |
| 49 | contig123 | 2-24 747 | 11 | t1pks | Unknown |
| 50 | contig125 | 1-24 065 | 24 | other | Melanin/黑色素 |
Note: t1pks: Type I polyketide synthase; t2pks: Type II polyketide synthase; t3pks: Type III polyketide synthase; nrps: Non ribosomal peptide; terpene: Terpenes; lant: Lantibiotics; ectoine: Four hydrogen pyrimidine; bcin: Bacteriocin; blactam: β-lactam.

|
| 图 3 Streptomyces sp. PRh5 次级代谢产物合成基因簇示意图(部分) Figure 3 Gene clusters sketch map involved in synthesis of secondary metabolites in Streptomyces sp. PRh5 (Partial) |
邓映明[16]从Streptomyces sp. PRh5的发酵液中分离得到邻苯二甲酸二丁酯、尼日利亚菌素、13-Docosenamide和诺卡胺素共4个化合物,其中尼日利亚菌素含量较高。尼日利亚菌素具有抗革兰氏阳性菌和真菌活性,并且生物合成途径已经阐 明[22]。此前文献报道尼日利亚菌素主要存在于菌体细胞内,然而PRh5菌株合成的尼日利亚菌素主要存在于胞外发酵液中,表明PRh5菌株具有较强的尼日利亚菌素外排能力。通过比较分析PRh5和已发表的尼日利亚菌素生物合成基因簇(GenBank accession No. DQ354110)发现,PRh5的尼日利亚菌素生物合成基因簇多出两个基因(图4和 表4),这可能是导致PRh5高产且分泌表达尼日利亚菌素的原因。

|
| 图 4 尼日利亚菌素合成基因族比较 Figure 4 Comparison of nigericin biosynthetic gene cluster |
| 编号 No. | 开发阅读框 ORF | 蛋白长度 Protein length | 功能 Fuction | 登录号 Accession No. |
| A | NigAV | 1 946 | Beta-ketoacyl synthase | EXU62069 |
| B | NigAVI | 1 666 | Beta-ketoacyl synthase | EXU62070 |
| C | 186 | Regulatory protein | EXU62080 | |
| D | TetR | 231 | TetR family transcriptional regulator | EXU62071 |
| E | NigCII | 288 | Alpha/beta hydrolase | EXU62072 |
| F | NigD | 419 | Cytochrome P450 | EXU62073 |
| G | NigAXI | 136 | Phosphopantetheine-binding protein | EXU62074 |
| H | NigAX | 1 288 | Polyketide synthase | EXU62075 |
| I | NigCI | 476 | Enterotoxin | EXU62076 |
| J | NigBIII | 155 | Hypothetical protein | EXU62077 |
| K | NigBI | 144 | Nuclear transport factor 2 | EXU62078 |
| L | NigAIX | 1 178 | Polyketide synthase | EXU62079 |
较土壤放线菌而言,植物内生放线菌研究较少且所处生境特殊,成为新菌株和天然活性化合物的新来源,在促生、抑制病虫害等方面具有广阔应用前景。Streptomyces sp. PRh5是一株从东乡野生稻中分离得到的对革兰氏阳性菌和真菌都具有较强抑制活性的内生放线菌。本实验室邓映明[16]采用琼脂扩散法检测PRh5菌株发酵液抑菌活性,结果显示发酵液对金黄色葡萄球菌和枯草杆菌具有很高的抑制活性;采用菌丝生长抑制法检测PRh5菌株发酵液对7种病源真菌抑制活性,结果显示对病源真菌较高的抑制活性,其中对油菜菌核病菌(Sclerotinia scleotiorum)抑制率高达86%。因此,对PRh5菌株进行全基因组测序有助于从分子水平上阐明抗性机制。
次级代谢产物是指微生物生长到一定阶段才产生的化学结构十分复杂、对该生物无明显生理功能或并非是微生物生长和繁殖所必需的物质。次级代谢产物包括聚酮(PK)、非核糖体肽(NRPS)、羊毛硫抗生素(Lantibiotics)、铁载体(Siderophores)、萜烯(Terpenes)等十几种。
链霉菌属是公认的次级代谢产物主要来源,本研究通过antiSMASH软件,首次在全基因组范围内分析Streptomyces sp. PRh5的次级代谢产物合成基因簇,共预测得到50个基因簇,为相关化合物的合成机制研究提供数据。另一方面,在对基因组背景信息了解的基础上,可通过基因工程技术,将次级代谢产物合成基因簇转移至不同的异源宿主中表达,不仅能够激活沉默的生物合成基因簇,而且可将异源表达体系作为一个非常有用的工具通过组合生物合成生产更多结构新颖、功能独特的化合物。
4 结论本研究采用高通量测序技术对Streptomyces sp. PRh5进行全基因组测序及分析,预测得到8 712个蛋白基因,50个次级代谢产物合成基因簇,并对基因簇可能合成的化合物进行了预测,包括美力霉素、雷弗霉素、弧菌铁素、疏螺旋体素、利迪链菌素、天冬霉素等十多种。同时,对尼日利亚菌素合成基因簇详细分析发现,PRh5的尼日利亚菌素基因簇较文献报道的多出两个基因,这可能是导致PRh5高效分泌合成尼日利亚菌素的原因。本研究的相关研究结果将为Streptomyces sp. PRh5的功能基因组学研究及相关次级代谢产物的生物合成途径及异源表达研究提供帮助。Streptomyces sp. PRh5基因组序列已提交至NCBI数据库,登录号为JABQ00000000。
| [1] | Hallmann J,Quadt-Hallmann A,Mahaffee W,et al.Bacterial endophytes in agricultural crops[J].Canadian Journal of Microbiology,1997,43(10):895-914 |
| [2] | Stone JK,Bacon CW,White J.An overview of endophytic microbes:endophytism defined[A]//Microbial Endophytes[M].New York:Marcel Dekker,2000:29-33 |
| [3] | Sturz A,Christie B,Nowak J.Bacterial endophytes:potential role in developing sustainable systems of crop production[J].Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences,2000,19(1):1-30 |
| [4] | Chen JK,Wang HY,He GQ.A survey on the habitats of Oryza rufipogon and Isoetes sinensis in Jiangxi Province[J].Chinese Biodiversity,1998,6(4):260-266 (in Chinese) 陈家宽, 王海洋, 何国庆.江西境内珍稀植物普通野生稻和 中华水韭产地的考察[J].生物多样性,1998,6(4):260-266 |
| [5] | Zhang CL,Huang YJ,Chen DZ,et al.Biochemical and physiological characteristics of cold tolerance for roots in dongxiang wild rice at the seedling stage[J].Review of China Agricultural Science and Technology,2007,9(2):49-52 (in Chinese) 张成良, 黄英金, 陈大洲, 等.东乡野生稻苗期根系耐冷性生 理生化特性[J].中国农业科技导报,2007,9(2):49-52 |
| [6] | Xie JK,Hu BL,Wan Y,et al.Comparison of the drought resistance characters at seedling stage between Dongxiang common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) and cultivars (Oryzasativa L.)[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2010(6):1665-1674 (in Chinese) 谢建坤, 胡标林, 万勇, 等.东乡普通野生稻与栽培稻苗期抗 旱性的比较[J].生态学报,2010(6):1665-1674 |
| [7] | Rosenblueth M,Martínez-Romero E.Bacterial endophytes and their interactions with hosts[J].Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions,2006,19(8):827-837 |
| [8] | Saikkonen K,Faeth S,Helander M,et al.Fungal endophytes:a continuum of interactions with host plants[J].Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics,1998,29:319-343 |
| [9] | Cragg GM,Newman DJ.Natural products:a continuing source of novel drug leads[J].Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects,2013,1830(6):3670-3695 |
| [10] | Strobel G,Daisy B.Bioprospecting for microbial endophytes and their natural products[J].Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews,2003,67(4):491-502 |
| [11] | Strobel G,Daisy B,Castillo U,et al.Natural products from endophytic microorganisms[J].Journal of Natural Products, 2004,67(2):257-268 |
| [12] | Strobel GA.Endophytes as sources of bioactive products[J].Microbes and Infection,2003,5(6):535-544 |
| [13] | Nakashima T,Okuyama R,Kamiya Y,et al.Trehangelins A,B and C,novel photo-oxidative hemolysis inhibitors produced by an endophytic actinomycete,Polymorphospora rubra K07-0510[J].The Journal of Antibiotics,2013,66(6):311-317 |
| [14] | Igarashi Y,Ogura H,Furihata K,et al.Maklamicin,an antibacterial polyketide from an endophytic Micromonospora sp.[J].Journal of Natural Products,2011,74(4):670-674 |
| [15] | Indananda C,Igarashi Y,Ikeda M,et al.Linfuranone A,a new polyketide from plant-derived Microbispora sp.GMKU 363[J].The Journal of Antibiotics,2013,66(11):675-677 |
| [16] | Deng YM.Study on identification and secondary metabolites of two endophytic actinomycetes from Dongxiang wild rice[D].Nanchang:Master's Thesis of Jiangxi Normal University,2014 (in Chinese) 邓映明.两株东乡野生稻内生放线菌的鉴定及代谢产物分离 [D].南昌:江西师范大学硕士论文,2014 |
| [17] | Zhu D,Deng YM,Zhang ZB,et al.A method of preparation two antibiotics using Streptomyces sp.:China,ZL2013106266697[P].2014-03-19 (in Chinese) 朱笃, 邓映明, 张志斌, 等.一种链霉菌及利用其制备两种抗 生素的方法:中国,ZL2013106266697[P].2014-03-19 |
| [18] | Zerbino DR,Birney E.Velvet:algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs[J].Genome Research,2008, 18(5):821-829 |
| [19] | Delcher AL,Bratke KA,Powers EC,et al.Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer[J].Bioinformatics, 2007,23(6):673-679 |
| [20] | Blin K,Medema MH,Kazempour D,et al.antiSMASH 2.0-a versatile platform for genome mining of secondary metabolite producers[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2013,41(Web Server issue):W204-W212 |
| [21] | Medema MH,Blin K,Cimermancic P,et al.antiSMASH:rapid identification,annotation and analysis of secondary metabolite biosynthesis gene clusters in bacterial and fungal genome sequences[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2011,39(Web Server issue):W339-W346 |
| [22] | Harvey BM,Mironenko T,Sun Y,et al.Insights into polyether biosynthesis from analysis of the nigericin biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces sp.DSM4137[J].Chemistry & Biology, 2007,14(6):703-714 |
 2015, Vol. 42
2015, Vol. 42




